Basal Insulin Is Responsible for Which of the Following Actions
Patients should be encouraged to self-manage insulin. Use of basal and bolus insulin together is intended to mimic the pancreas production of endogenous.
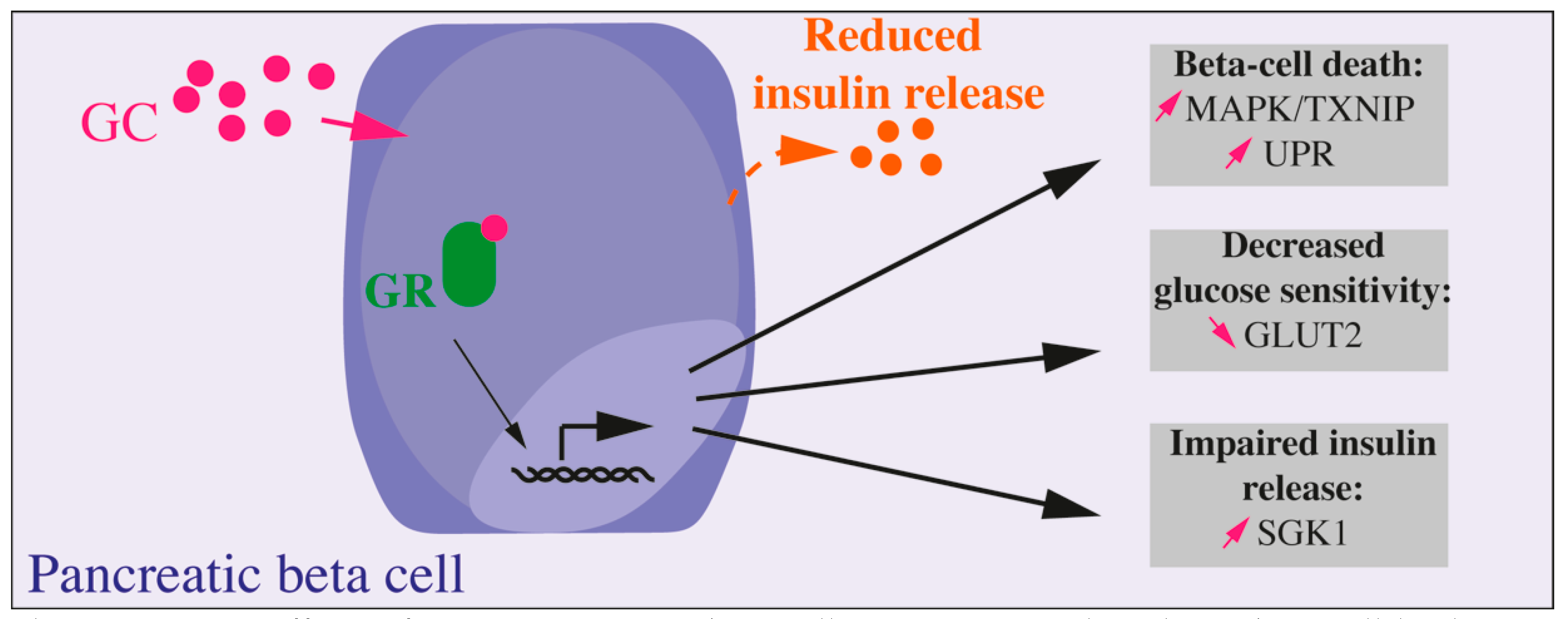
Ijms Free Full Text Molecular Mechanisms Of Glucocorticoid Induced Insulin Resistance Html
Insulin decreases plasma glucose concentration in what three ways.
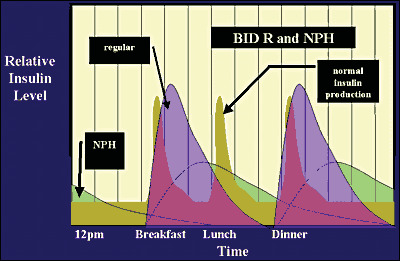
. In general basal insulin. Recommendations on initiation and intensification of basal insulin and its use in special situations have been developed. Suppression of hepatic glucose production B.
Bolus insulin is often combined with once daily long-acting basal insulin such as Insulin detemir Insulin degludec and Insulin glargine to provide low concentrations of background insulin that can keep blood sugar stable between meals or overnight. Insulin serves to lower the blood glucose level by stimulating the uptake of glucose by cells specifically muscle cells liver cells and adipose tissue. The primary job of basal insulin is to keep your blood glucose levels stable during periods of fasting such as while youre sleeping.
If a patient is paying more than 25 a vial for NPH insulin I. Basal insulin when used correctly is responsible for which of the following actions. This is substantially cheaper than the branded basal insulins.
Depending on which delivery mechanism is used the basal can be a long-acting insulin or a rapid-acting insulin while boluses will always be rapid-acting or short-acting insulin more about the. Basal insulin is longer-acting and helps keep your glucose levels steady day and night. The primary job of basal insulin is to keep your blood glucose levels stable during periods of fasting such as while youre sleeping.
Basal insulin helps glucose control. Insulin suppresses hepatic glucose production stimulates glucose uptake in muscle suppresses adipose tissue lipolysis and fatty acid release into the blood stream. Protein synthesis cell division DNA synthesis.
The patient should be paying no more than 25 per 1000-U vial. Long-acting basal- insulin glargine Lantus and detemir Levemir administered once or twice a day do not mix with any other insulin or solution. Lack of a standardised insulin dose titration regime may be responsible and unstructured regimens may in turn lead to excessive basal insulin doses and between meal hypoglycaemia.
The primary job of basal insulin is to keep your blood glucose levels stable during periods of fasting such as while youre sleeping. Insulin also promotes growth and is required for the actions of growth hormone eg. Persons with type 1 diabetes generally use intermediate-acting insulin or long-acting insulin in conjunction with regular or rapid acting.
Correct initiation titration and where appropriate switching between preparations can facilitate good control of FPG. Increase in ketone production. Summary of the major metabolic actions of insulin.
Basal insulin keeps these glucose levels under control. It keeps glucose levels constant throughout the day and night. Basal insulin absorbs slowly and is long-lasting which helps keep your blood sugar level stable when your liver releases extra glucose.
Doctors now call basal-bolus therapy intensive or flexible insulin. Background and aims Clinical inertia is reported to delay insulin dose intensification in type 2 diabetes patients. Increase in fatty acid production D.
Cloudy must agitate to mix. Basal Insulin Types Benefits Dosage Information And Side Effects. Regardless of type of diabetes those needing multiple daily injections will need background insulin basal as well as insulin to cover meals and corrections bolus.
Basal insulin is often required in the management of T2D. Used to control glucose levels between meals and overnight. It is used to mimic the basal levels of insulin in diabetic individuals.
The key recommendations are to initiate basal insulin when 2 or 3 oral antidiabetic medications fail to achieve target glycaemic control or in symptomatic patients with glycated haemoglobin value greater than 9. Suppresses hepatic apolipoprotein B-100 and triglyceride secretion stimulates lipoprotein lipase activity in adipose tissue and inhibits protein. Generally your total daily dosage of injected insulin is split between these short- and longer-acting kinds.
While fasting your liver continuously secretes glucose into the bloodstream. The insulin reaches the bloodstream several hours after injection. Insulin glargine is a long-acting insulin analogue with a flat and predictable action profile.
Basal-Bolus therapy involves combining a longer-acting or basal insulin analog together with separate injections of a shorter-acting or bolus insulin analog. Intermediate- and long-acting basal insulins are recommended for patients with type 1 type 2 or gestational diabetes. Reduction of glucose concentrations after meals C.
Basal Insulins Intermediate and Long-Acting Who. A turning it into ATP protein and fats B uptake of glucose into the cells converting it to glycogen and increasing gluconeogenesis. Basal Insulin Types Benefits Dosage Information And Side Effects.
Basal insulin keeps these glucose levels under control. Basal-bolus insulin therapy is an option for diabetes management that combines different types of short- and long-acting insulin. While fasting your liver continuously secretes glucose into the bloodstream.
The role of basal insulin also known as background insulin is to keep blood sugar levels stable throughout the day and allow your body to take in sugar used for energy for all of the. Basal insulins have greatly evolved from traditional NPH to first generation basal insulin analogues glargine 100umL detemir and now to the next generation of basal insulin analogues glargine 300 umL degludec. They may also be used in other types of diabetes ie.
Intermediate- acting- duration 12-18 hrs peak 4-12 hrs can mix with short- and rapid-acting insulin.

Insulin Pharmacology Therapeutic Regimens And Principles Of Intensive Insulin Therapy Endotext Ncbi Bookshelf

Adding Fast Acting Insulin Aspart To Basal Insulin Significantly Improved Glycaemic Control In Patients With Type 2 Diabetes A Randomized 18 Week Open Label Phase 3 Trial Onset 3 Rodbard 2017 Diabetes
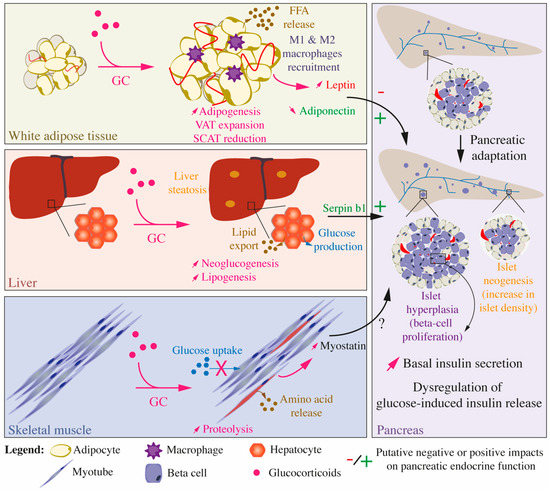
Ijms Free Full Text Molecular Mechanisms Of Glucocorticoid Induced Insulin Resistance Html

Insulin Therapy For Type 2 Diabetes Patients Dr Shahjadaselim1
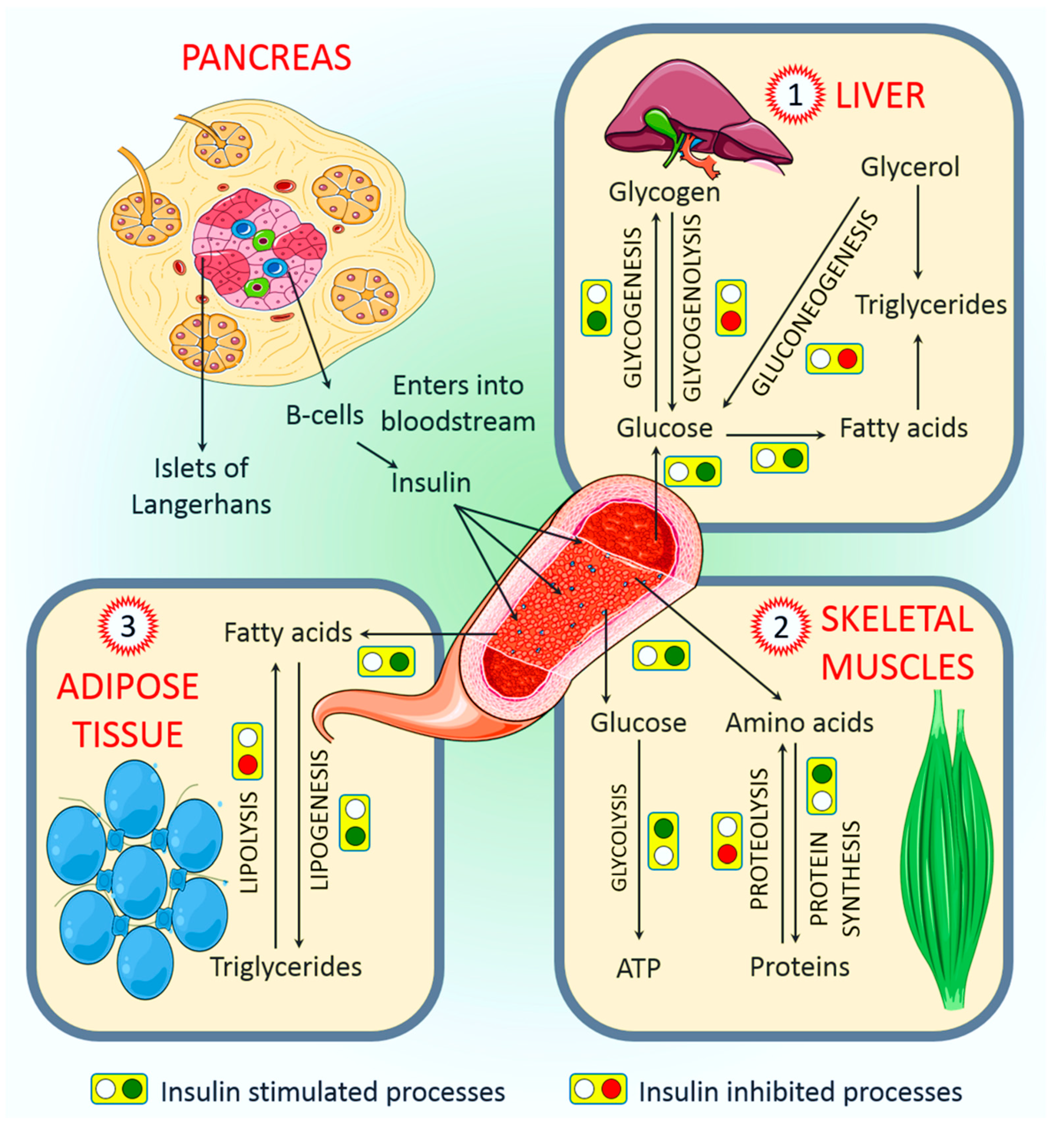
Ijms Free Full Text Role Of Insulin In Health And Disease An Update Html
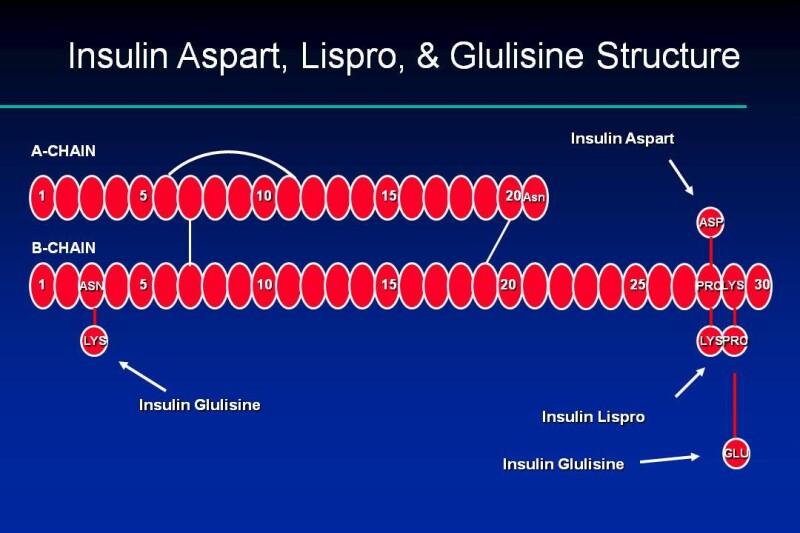
Insulin Pharmacology Therapeutic Regimens And Principles Of Intensive Insulin Therapy Endotext Ncbi Bookshelf
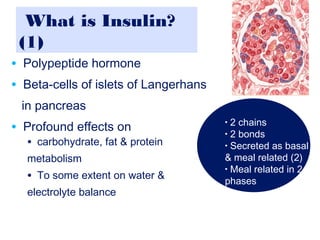
Insulin Therapy For Type 2 Diabetes Patients Dr Shahjadaselim1

Insulin Therapy For Type 2 Diabetes Patients Dr Shahjadaselim1
Insulin Secretory And Antidiabetic Actions Of Heritiera Fomes Bark Together With Isolation Of Active Phytomolecules

Insulin Therapy For Type 2 Diabetes Patients Dr Shahjadaselim1

Insulin Pharmacology Therapeutic Regimens And Principles Of Intensive Insulin Therapy Endotext Ncbi Bookshelf
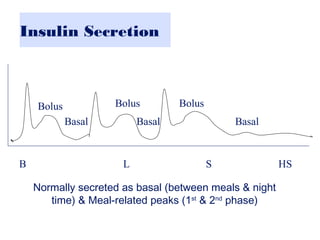
Insulin Therapy For Type 2 Diabetes Patients Dr Shahjadaselim1
Basal Bolus What Is Basal Insulin Bolus Insulin

Insulin Analog Therapy Improving The Match With Physiologic Insulin Secretion

Insulin Analog Therapy Improving The Match With Physiologic Insulin Secretion
Insulin Secretory And Antidiabetic Actions Of Heritiera Fomes Bark Together With Isolation Of Active Phytomolecules
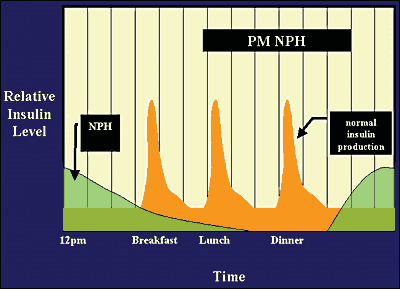
Insulin Pharmacology Therapeutic Regimens And Principles Of Intensive Insulin Therapy Endotext Ncbi Bookshelf
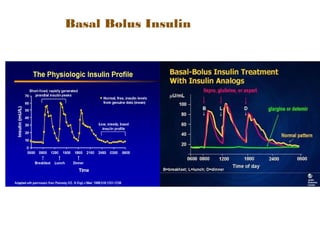
Comments
Post a Comment